Modern energy-efficient modular homes are growing in popularity because they are a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional residential construction. As the prices for homes continue to skyrocket, affordable housing is a priority for those looking to buy a new home.
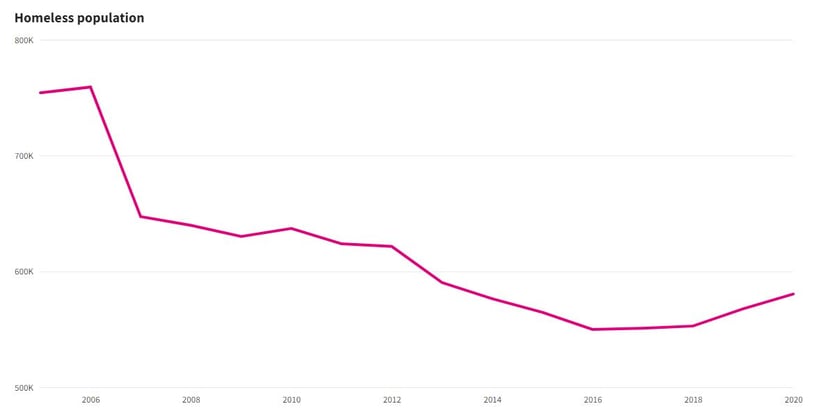
The homeless population is now more than 580,000 in the United States. Over the last five years, there has been a steady climb in homelessness. It is nearly as high as during the housing crisis in 2008.
In the past, people associated homelessness with addiction and mental illness. Today entire families are living in tents on the side of the streets.
Economists attribute this financial crisis to inflation and the pandemic. The prices of houses have increased more than 20% in the last year, making it difficult for the middle-class to own a home.
Modular homes are the answer to the current housing crisis because it makes homeownership more affordable for everyone. Here's what you need to know about what goes into energy-efficient modular homes.
Key Takeaways:
- Modular homes are prefabricated houses constructed off-site in a factory and shipped to the location where developers assemble the structure according to the housing plan.
- These homes differ from manufactured homes because developers construct modular homes on permanent foundations while developers set manufactured models on chassis that can move.
- There are six elements of an energy-efficient modular home. They include site design, assembly, sealing, windows and doors, ventilation, and HVAC systems.
What is a Modular Home?
Modular homes are similar to traditional homes. Developers place these houses on a permanent foundation. Yet, contractors partially construct these houses in a factory and ship them to the homeowner’s lot.
The modular home construction must comply with regional standards of building codes. In most cases, it's difficult to tell the difference between a traditional site-built house and a modular home.
Many people confuse modular homes with manufactured homes. These are two different types of construction. Let's take a moment to review some of the significant differences between these homes.
How Modular Homes Differ from Manufactured Homes
Manufactured and modular houses are each constructed off-site. Yet, the primary difference is that while developers assemble modular homes on permanent foundations, they place manufactured models on chassis. These homes can move from one site to another if the homeowner purchases another property.
Local, regional, and state building codes differ with each structure. Also, manufactured homes must adhere to the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) federal codes.
6 Elements of Energy-Efficient Modular Homes
The design and development of energy-efficient modular homes are challenging. Yet, with the rise in energy costs and sustainability demands from those looking to buy a home, it becomes a challenge developers must meet. Here are the six primary elements in energy-efficient modular homes designs:
1. Site Design
Sustainability in modular homes begins with site selection. Developers must evaluate each location with consideration for the potential orientation of the house. That way, it can benefit from a passive solar design.
Additionally, site selection should include how the home fits into the surrounding ecosystem. Cost-effective, energy-efficient modular home design must also consider access to transportation, services, and rapid transit.
2. Assembly
In an energy-efficient structure, walls and roofs must be well insulated. Also, the materials should promote sustainability. For example, designers will use reclaimed wood panels for making walls from timber offcuts.
For roofing, developers create a green roof (also known as a living roof). The material used consists of waterproof membranes and soil. These roofs:
- Are durable and eco-friendly
- Lessen cool air loss
- Improve air quality
- Provide more insulation
- Reduce outside noise
You can also find bio-based materials created from agricultural waste for structural insulated panels and sheathing products. Manufacturers also use these materials to make walls. This new technology continues to gain ground in modular home materials because they provide energy efficiency in affordable and durable products.
3. Air-Sealing and Insulation
You must provide an effective external thermal envelope for sustainable modular home construction. For that reason, developers must prioritize air-sealing and insulation for these structures.
So, ensure the home is well sealed at all joints and properly insulated. Check the following to ensure the modular home is well-insulated:
- Inspect windows, doors, and wall joints for drafts
- Look for moisture buildup and leaks
- Check for varying inside temperatures
4. Windows and Doors
More than 30% of a structure's cooling and heating loss comes from windows and doors. All portals of a modular home must not only be well-sealed, but they must also have energy-efficient windows and doors installed.
Improvements in window and door design technology reduce the transfer of this energy. Material and coatings keep the elements out while ensuring the temperature inside the home remains stable.
Also, consider the orientation of the home. South-facing windows should get the benefits of passive solar designs while you can maximize heat transfer from the other side of the structure.
5. Ventilation
Proper ventilation ensures the air quality inside the building and improves efficiency. You can utilize heat recovery ventilators that use heat exchangers to recover any loss of heat through conventional ventilation systems.
These systems do not blow the warm, stale air into the environment. Instead, it traps, recirculates, and warms the air inside in an energy-efficient way, reducing energy consumption and waste.
6. HVAC Systems
At the heart of any energy-efficient building design is the HVAC system. These systems burn the most energy of others within the home. That is why it is vital to install an Energy Star HVAC unit in your modular home design.
You want to ensure that you install an HVAC system that meets the needs for heating and cooling the size of the home. However, with the proper orientation of the modular home, you can take advantage of a passive solar design and use a smaller HVAC unit.
The Finishing Touches to Modular Home Designs
Energy-efficient modular homes require sustainable fittings, fixtures, and plumbing systems to be truly environmentally friendly dwellings.
Before construction is complete on your next modular home design, consider installing Geberit's sustainable plumbing systems. These finishing touches will make your next modular project more eco-conscious and better for the environment.
If you're designing a modular home, contact us here to learn more about our sustainable sanitation systems.